Entamoeba histolytica laboratory diagnosis
Traditional O&P examinations / microscopy:
Whilst traditional microscopy continues to be used to identify Entamoeba, this method cannot differential between E. histolyica and non-pathogenic species of Entamoeba. Microscopy is considered less reliable than either culture, immunoassays or molecular methods [6]. Confirmation testing by ELISA or PCR are required for microscopy results [7].
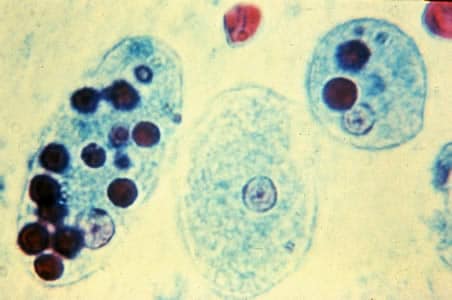
Diagnostic for E. histolytica (true pathogen) requires identification of red blood cells on the slide, due to trophozoites ingesting red blood cells.
Image credit: CDC www.cdc.gov/dpdx/amebiasis/index.html
Trophozoites of E. histolytica with ingested erythrocytes stained with trichrome. The ingested erythrocytes appear as dark inclusions.
Types of Immunoassays:
- Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA): Detects E. histolytica-specific antigens in stool or antibodies in serum.
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests (RDTs): Lateral flow immunoassays for quick detection of antigens in stool. Other parasite such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium may also be tested simultaneously with E. histolytica.
Other diagnostic modalities used in clinical laboratories include serology, and colonoscopy with a histologic examination.
Molecular methods for detecting E. histolytica (true pathogen)
Molecular techniques have the highest sensitivity, including the ability to distinguish between morphologically identical E. histolytica (true pathogen) and E. dispar.
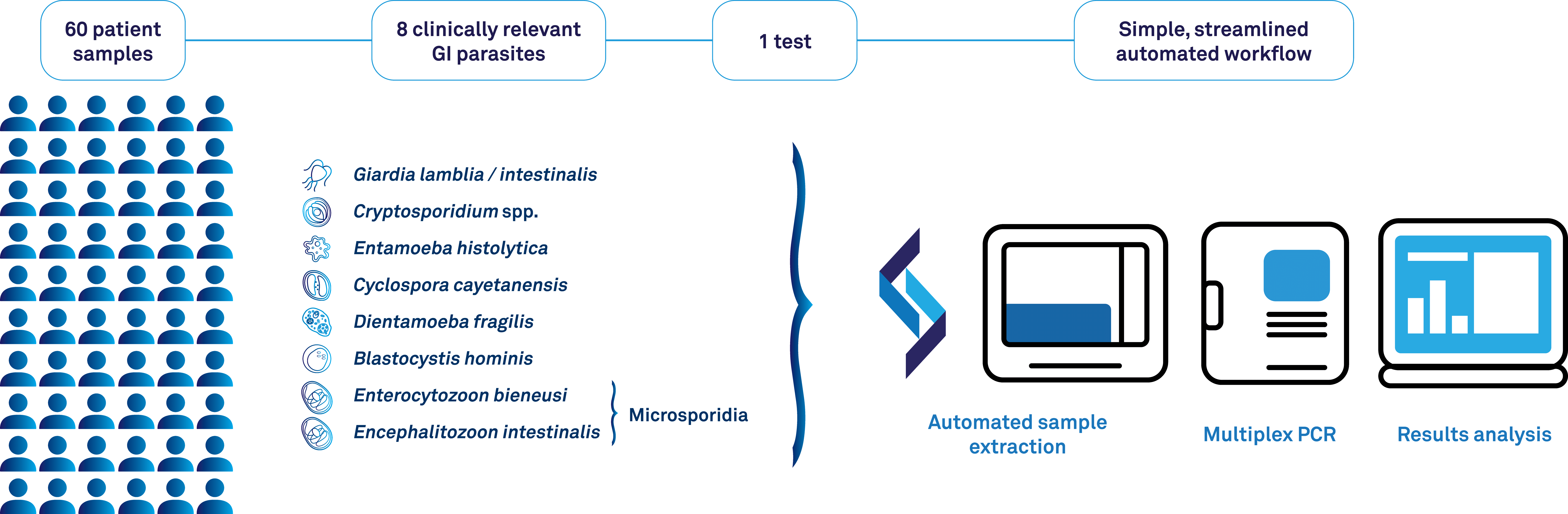
Currently, Genetic Signatures EasyScreen™ Gastrointestinal Detection Kit is the only FDA 510(k) cleared molecular diagnostic solution available that can detect E. histolytica, together with 7 other leading gastrointestinal parasites, in the same test.
View the recent webinar highlighting the benefits of molecular solutions for detecting these key gastrointestinal parasites, featuring leading parasitologists
Syndromic testing for 8 gastrointestinal parasites in a single test
Up to 60 patients screened in a single, automated workflow...with same day reporting!