Microsporidiosis: symptoms, prevention & treatment
Microsporidiosis symptoms
Symptoms of infection from E. bieneusi or E. intestinalis
People with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of microsporidia infections. Symptoms in these individuals can be more severe and may involve multiple organ systems.
Diarrhea and malabsorption seem to be the most common clinical problems associated with microsporidian infections. Gastrointestinal symptoms include:
- Watery and sometimes persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal Cramping and discomfort in the abdomen.
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Weight Loss due to chronic diarrhea and poor nutrient absorption.
- Malabsorption
Microsporidia can be an important cause of persistent diarrhea, intestinal malabsorption, and wasting in HIV-positive adults. Mucosal damage associated with microsporidiosis is more extensive than that related to other opportunistic intestinal infections and leads to substantial malabsorption of vitamins, micronutrients, carbohydrates, and fats [1-5].
The benefits of employing molecular syndromic testing for overlapping gastrointestinal signs and symptoms
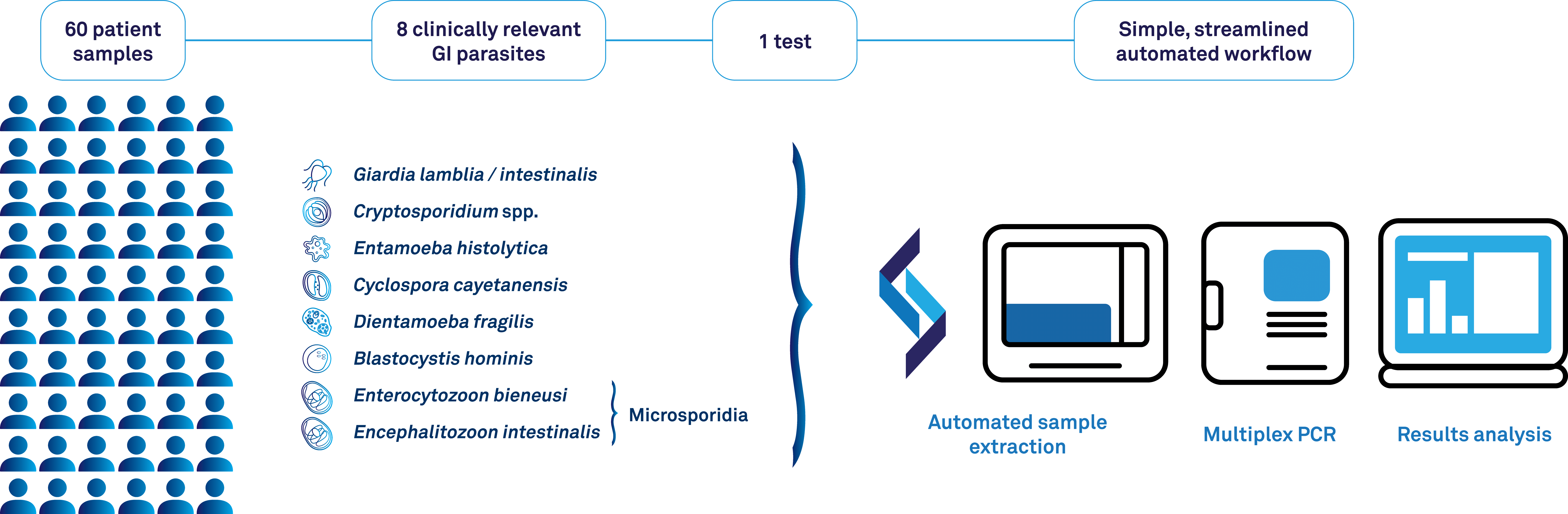
Genetic Signatures' EasyScreen Gastrointestinal Parasite Detection Kit can detect 8 parasite pathogens from a single sample, in a single test, increasing the likelihood of identifying co-infections from multiple parasites that might be missed with traditional testing methods. This is particularly important in cases where patients present with non-specific or overlapping symptoms that could be caused by a variety of gastrointestinal pathogens.
Preventing microsporidiosis
Like all gastrointestinal pathogens, preventing infection from microsporidia primarily involves maintaining good hygiene, ensuring safe water consumption, and practicing safe food handling.
There must be protective measures for immunocompromised individuals and additional precautions considered to avoid microsporidia spores.

Treatment for microsporidia infection
Treatment of microsporidiosis typically includes a combination of antiparasitic medication and supportive healthcare to address symptoms such as preventing dehydration and nutritional support.
As this infection often occurs in immunocompromised patients, the patient's immune status and existing treatment plan is a key consideration.
Treatment challenge:
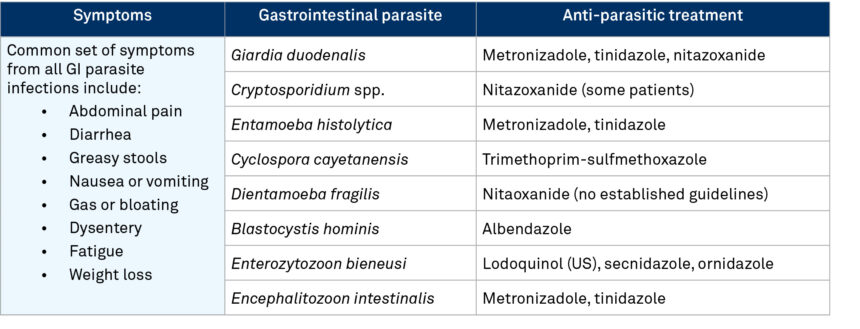
Treatment of gastrointestinal parasite infections is challenging due to parasite diversity and their specific treatment requirements, despite causing common symptoms (see table below). Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment. In addition, misuse or overuse of anti-parasitic drugs can lead to the development of antimicrobial resistance. Thus, timely and accurate detection of parasitic pathogens can support appropriate patient management and improve health outcomes.
Syndromic testing for 8 gastrointestinal parasites in a single test
Up to 60 patients screened in a single, automated workflow...with same day reporting!
Find out more about our unique 3base™ solution for detecting gastrointestinal parasites
References
- Lynne Garcia (2023). Genetic Signatures. Advances in Gastrointestinal Parasite Testing webinar series.
- Matos O, Lobo ML, Xiao L. Epidemiology of Enterocytozoon bieneusi Infection in Humans. J Parasitol Res. 2012;2012:981424. doi: 10.1155/2012/981424. Epub 2012 Oct 3. PMID: 23091702; PMCID: PMC3469256.
- Weber R, Ledergerber B, Zbinden R, et al. Enteric infections and diarrhea in human virus-infected persons: prospective community-based cohort study. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1999;159(13):1473–1480.
- Kotler DP, Francisco A, Clayton F, Scholes JV, Orenstein JM. Small intestinal injury and parasitic diseases in AIDS. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1990;113(6):444–449.
- Greenson JK, Belitsos PC, Yardley JH, Bartlett JG. AIDS enteropathy: occult enteric infections and duodenal mucosal alterations in chronic diarrhea. Annals of Internal Medicine. 1991;114(5):366–372.
More Information
Click to learn more about the parasites we detect
References
- Laksemi DA, Suwanti LT, Mufasirin M, Suastika K, Sudarmaja M. Opportunistic parasitic infections in patients with human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: A review. Vet World. 2019 Apr;13(4):716-725. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.716-725. Epub 2020 Apr 17. PMID: 32546916; PMCID: PMC7245710.
- Aghazadeh M, Jones M, Perera S, Nair J, Tan L, Clark B, Curtis A, Jones J, Ellem J, Olma T, Stark D, Melki J, Coulston N, Baker R, Millar D. The Application of 3base™ Technology to Diagnose Eight of the Most Clinically Important Gastrointestinal Protozoan Infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13387. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713387. PMID: 37686192; PMCID: PMC10487386. Aghazadeh M, Jones M, Perera S, Nair J, Tan L, Clark B, Curtis A, Jones J, Ellem J, Olma T, Stark D, Melki J, Coulston N, Baker R, Millar D. The Application of 3base™ Technology to Diagnose Eight of the Most Clinically Important Gastrointestinal Protozoan Infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 29;24(17):13387. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713387. PMID: 37686192; PMCID: PMC10487386.
- Sadaf, H.S., Khan, S.S., Urooj, K.S., Asma, B. and Ajmal, S.M. (2013) Blastocystis hominis-potential diahorreal agent: A review. Res. J. Pharm., 4(1): 1-5.